Optimal Seafood Choices During Pregnancy
When considering the best types of fish to eat during pregnancy, one should prioritise those rich in Omega-3 fatty acids while low in mercury. Salmon, tilapia, shrimp, pollock, catfish, and light tuna stand out as excellent choices. These varieties offer substantial health benefits without the heightened risk of mercury exposure that can be detrimental to foetal development.
The Role of Omega-3 in Foetal Development
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), are pivotal for the neurocognitive development of the foetus. They contribute significantly to the formation of the brain and retina, influencing visual and cognitive functions.
Selecting Low-Mercury Fish for Prenatal Nutrition
The selection of low-mercury fish is crucial during pregnancy. High levels of mercury can adversely affect the developing nervous system of the foetus. Therefore, it is imperative to avoid fish known for high mercury content, such as shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish, and instead opt for safer options recommended by health authorities.
Ensuring Quality and Safety with “Frozen Fish Direct”
Frozen Fish Direct” is committed to providing pregnant women with high-quality and safe seafood options. They ensure that all seafood meets stringent safety standards, preserving the nutritional integrity while minimising the risk of contaminants. By sourcing from reputable suppliers and adhering to rigorous food safety protocols, “Frozen Fish Direct” stands as a reliable source for nutrient-rich seafood suitable for pregnancy.
The Essential Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Pregnancy

Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), are pivotal for neurocognitive development during pregnancy. DHA contributes to the formation of the cerebral cortex and retina, influencing visual and cognitive functions in the foetus. EPA supports these processes by reducing inflammation, which is crucial for creating a conducive environment for neuronal growth.
Impact on Maternal Health and Mood
The intake of omega-3 fatty acids has been linked to improved maternal health, with studies suggesting a correlation between omega-3 consumption and a reduction in the risk of perinatal depression. The anti-inflammatory properties of EPA can enhance mood regulation, providing a sense of well-being during pregnancy.
Comparing Fish and Supplement Sources
While both seafood and supplements can provide omega-3 fatty acids, the bioavailability of these nutrients is generally higher in whole fish. Seafood not only delivers DHA and EPA but also comes with additional nutrients beneficial for pregnancy, such as iodine and selenium.
Omega-3 Levels: Fish vs. Non-Seafood Sources
Fish are the most efficient source of omega-3 fatty acids, with fatty species like salmon and mackerel containing higher levels compared to non-seafood sources. Plant-based alternatives, such as flaxseeds and walnuts, contain alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which the body must convert to DHA and EPA, albeit at a lower conversion rate.
FDA and EPA Seafood Consumption Guidelines

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommend that pregnant individuals consume 8-12 ounces of low-mercury seafood per week. This guideline is designed to maximise the intake of essential nutrients while minimising exposure to potential toxins.
Balancing Nutrition and Safety
These recommendations ensure a balance between obtaining critical nutrients for foetal development, such as omega-3 fatty acids, and safeguarding against the neurotoxic effects of mercury. The agencies have categorised seafood into “Best Choices,” “Good Choices,” and those to avoid, to simplify safe consumption.
Global Considerations for Seafood Consumption
Globally, seafood consumption advisories vary based on local marine life and pollution levels. For instance, the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) and the Australian Dietary Guidelines provide tailored advice reflecting regional seafood profiles and environmental conditions.
Alignment with “Frozen Fish Direct” Standards
“Frozen Fish Direct” aligns with these health guidelines by offering a selection of seafood that falls within the “Best Choices” category. They ensure that their products meet the safety standards set by regulatory bodies, providing customers with both nutritious and safe options for their prenatal dietary needs.
Identifying High-Mercury Fish Species

Certain fish species are known to accumulate higher levels of mercury due to their diet and position in the food chain. Pregnant women are advised to avoid shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish due to their elevated methylmercury content, which poses risks to foetal neurodevelopment.
Minimising Mercury Exposure
To minimise the risk of mercury exposure, pregnant women should focus on consuming a variety of seafood that is low in mercury, such as salmon, tilapia, shrimp, pollock, catfish, and canned light tuna. Adhering to the FDA and EPA guidelines of 8-12 ounces per week helps maintain a safe intake level.
Understanding the Effects of Mercury
Long-term exposure to high levels of mercury can lead to developmental delays and cognitive deficits in children. For pregnant women, excessive mercury intake can increase the risk of cardiovascular complications.
“Frozen Fish Direct” Commitment to Safety
“Frozen Fish Direct” assists consumers in making informed choices by providing transparency about the mercury content in their seafood offerings. They source from trusted suppliers and regularly test their products to ensure compliance with safety standards, thereby helping customers avoid high-mercury seafood.
Heeding Local Fish Advisories During Pregnancy

Local fish advisories play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of seafood consumed during pregnancy. These advisories provide location-specific information on seafood that may be contaminated with pollutants, such as mercury or polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), which can adversely affect foetal development.
Impact of Advisories on Seafood Selection
For pregnant women, adhering to these advisories is essential to avoid the intake of harmful substances. Local advisories often list which fish are safest to eat, which to eat in moderation, and which to avoid, allowing for informed decisions that prioritise both nutritional benefits and safety.
Resources for Verifying Seafood Safety
To check the safety of local seafood, resources such as government health department websites, environmental agencies, and local fishing bulletins are invaluable. These platforms regularly update advisories based on the latest testing and research.
“Frozen Fish Direct” Compliance with Advisories
“Frozen Fish Direct” remains vigilant regarding local fish advisories by sourcing seafood from uncontaminated waters and conducting rigorous quality checks. They ensure their offerings align with the latest safety recommendations, providing customers with peace of mind when selecting seafood for their prenatal diet.
Safe Seafood Preparation During Pregnancy

When preparing seafood during pregnancy, safety is paramount. Proper cooking techniques can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illness, which is especially important for the health of both the expectant mother and the developing foetus.
Best Practices for Cooking Seafood
To ensure safety, seafood should be cooked to an internal temperature of 145F, at which point the flesh becomes opaque and separates easily with a fork. This guideline applies to finfish, while shrimp, lobster, and scallops should be cooked until milky white. Clams, mussels, and oysters should be cooked until their shells open, discarding any that do not.
Preventing Health Risks Through Proper Preparation
Avoiding raw and undercooked seafood is crucial, as it may contain harmful bacteria and viruses. Pregnant individuals should also abstain from refrigerated, uncooked seafood, such as smoked seafood, unless it is contained within a cooked dish or processed to eliminate pathogens.
Guidance from “Frozen Fish Direct”
“Frozen Fish Direct” provides customers with detailed preparation instructions to ensure the seafood they consume is safe. They emphasise the importance of following recommended cooking temperatures and techniques, and offer resources to educate on the proper handling and storage of seafood products. This guidance is designed to help you enjoy the nutritional benefits of seafood while minimising any potential health risks.
Exploring Non-Seafood Omega-3 Options for Expectant Mothers
For pregnant women who prefer not to consume fish or are seeking alternative omega-3 sources, a variety of options are available. Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are plant-based foods rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which the body can convert to EPA and DHA, albeit at a lower efficiency compared to fish sources.
Omega-3 Supplements Versus Whole Fish
Omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil capsules, offer a concentrated source of DHA and EPA. While these supplements can be effective, the bioavailability of omega-3s is generally higher when sourced from whole fish due to the presence of other nutrients that aid in absorption.
Considerations for Vegetarians and Individuals with Fish Allergies
Vegetarians and those with fish allergies can opt for algae-based supplements, which provide DHA and EPA without the need for fish or animal products. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure these alternatives meet the nutritional needs of both the mother and the developing foetus.
“Frozen Fish Direct” Support for Diverse Dietary Needs
“Frozen Fish Direct” caters to a wide range of dietary preferences by offering not only high-quality seafood but also providing information on alternative omega-3 sources. They are committed to supporting the health of all customers, including those who require non-seafood options for their prenatal nutrition.
Guiding Safe Seafood Choices in Pregnancy

Healthcare providers are instrumental in guiding pregnant women through the complexities of seafood consumption. They can offer personalised advice based on the latest research and official dietary guidelines, ensuring that expectant mothers receive the full neurocognitive benefits of omega-3 fatty acids while minimising exposure to mercury.
Educational Resources for Seafood Consumption
Clinicians have access to a wealth of educational materials, including brochures, websites, and detailed dietary guidelines from organisations like the FDA and EPA. These resources can help demystify the nutritional science behind seafood and provide clear, actionable advice for pregnant women.
Addressing Mercury Misconceptions
Healthcare providers play a key role in dispelling myths about mercury in fish. By explaining the differences between high-mercury and low-mercury fish and emphasising the importance of variety and moderation, they can alleviate concerns and promote a balanced diet.
“Frozen Fish Direct” Support for Clinicians
Frozen Fish Direct” aids healthcare professionals by supplying accurate information on the sourcing and safety of their seafood products. This transparency allows clinicians to confidently recommend “Frozen Fish Direct” as a trusted provider of high-quality, low-mercury seafood options for their patients’ prenatal diets.
Comprehensive Nutritional Benefits of Seafood for Expectant Mothers
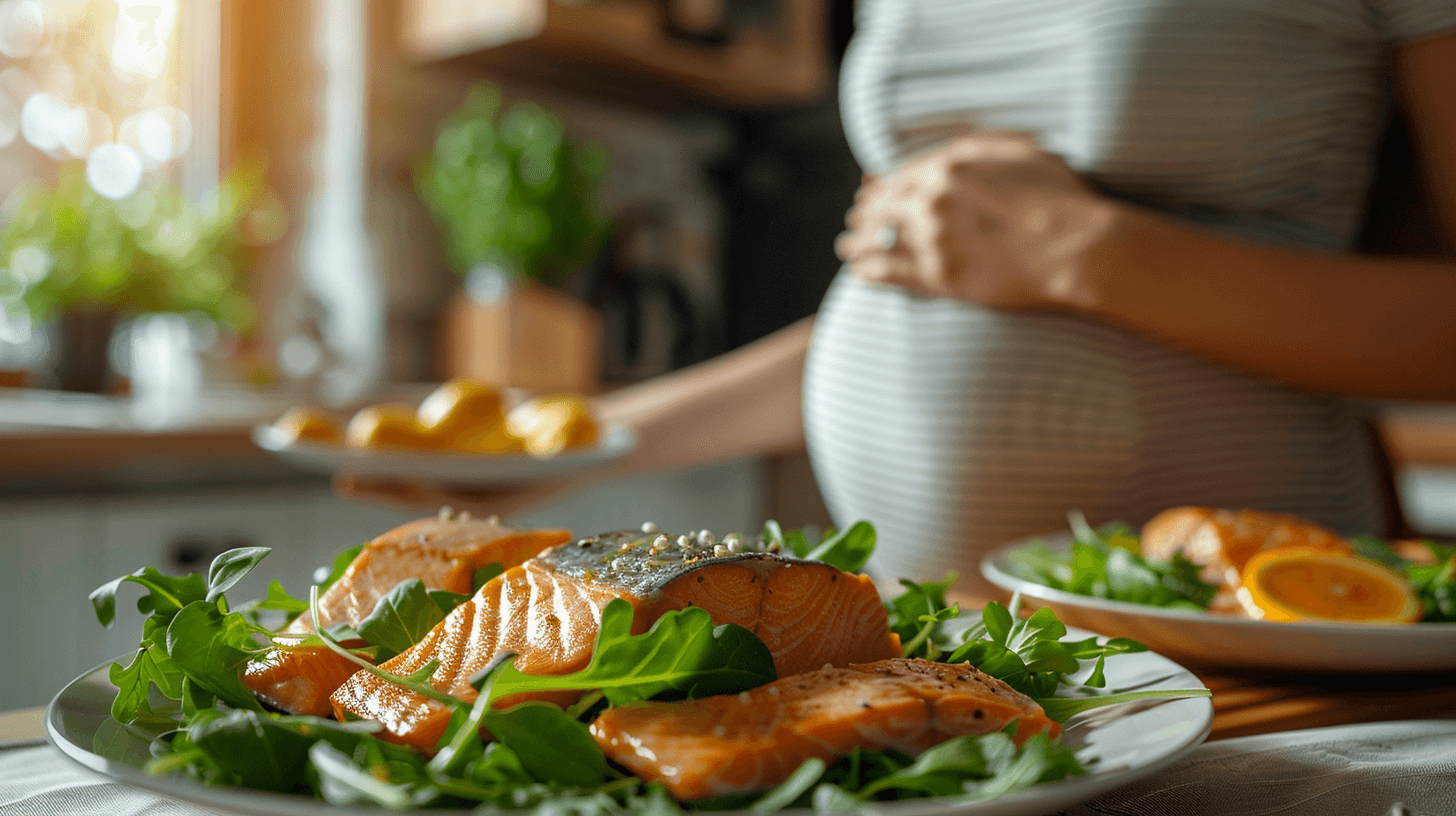

Seafood is a nutritional powerhouse, particularly beneficial for those who are pregnant due to its rich profile of essential nutrients that support prenatal health.
Protein and Pregnancy Dietary Requirements
The high-quality protein found in fish is vital for the growth and repair of tissues, which is crucial during pregnancy. It provides the amino acids necessary for the development of the foetus and the health of the mother.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals in Seafood
Seafood is an excellent source of vitamins and minerals that play a significant role in prenatal health:
- Vitamin B12: Crucial for maintaining the health of nerve cells and aiding in the production of DNA and RNA.
- Vitamin D: Supports immune function and bone health, and is essential for the absorption of calcium.
- Selenium: Acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
- Iodine: Necessary for the proper function of the thyroid gland, which regulates growth and metabolism.
- Choline: Supports brain development and liver function.
“Frozen Fish Direct” Commitment to Nutritional Diversity
“Frozen Fish Direct” ensures a diverse nutritional profile in its seafood offerings by sourcing a wide variety of fish, each with its unique set of nutrients. They provide detailed information on the nutritional content of their products, allowing you to make informed choices that align with your dietary needs during pregnancy.
Nutritional Psychiatry: Seafood’s Role in Maternal Mental Health
Emerging research in nutritional psychiatry suggests that the omega-3 fatty acids found in seafood, particularly DHA and EPA, may have a protective effect against prenatal depression. These essential nutrients are believed to contribute to the structural integrity of brain cells and support neurotransmitter function, which can influence mood and emotional well-being.
Seafood Nutrients and Mood Improvement
The relationship between fish nutrients and maternal mood is supported by the anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 fatty acids. Chronic inflammation has been linked to depression, and by reducing inflammation, omega-3s can potentially improve mood and alleviate symptoms of depression during pregnancy.
Diet’s Influence on Mental Health During Pregnancy
Diet plays a critical role in mental health, especially during pregnancy. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids from seafood has been associated with lower levels of anxiety and depression, suggesting that these nutrients may help to stabilise mood and enhance emotional resilience.
“Frozen Fish Direct” and Mental Well-Being
“Frozen Fish Direct” supports mental well-being through diet by providing access to a variety of high-quality, omega-3-rich seafood. They ensure that their products are sourced sustainably and contain the nutrients necessary to support maternal mental health, making it easier for you to incorporate these beneficial foods into your prenatal diet.
Sustainable Seafood: A Keystone of Environmental Health

Sustainable seafood sourcing is vital for maintaining healthy marine ecosystems and ensuring the long-term viability of fish populations. By choosing sustainable seafood, consumers play a direct role in promoting environmentally friendly fishing practices.
Impact on Marine Ecosystems
The selection of sustainable fish helps to prevent overfishing, supports species diversity, and maintains the balance of aquatic environments. It also minimises the bycatch of unintended species and reduces the impact on marine habitats.
Best Practices for Responsible Seafood Sourcing
Responsible seafood sourcing involves:
- Choosing certified sustainable seafood: Look for certifications from organisations like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) or the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC).
- Supporting local fisheries: This often means fresher options and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Being informed: Understanding seasonal fish availability and the environmental impact of different fishing methods.
“Frozen Fish Direct” Commitment to Sustainability
Frozen Fish Direct” demonstrates its commitment to sustainability by:
- Sourcing responsibly: They prioritise suppliers who adhere to strict environmental standards.
- Transparency: Providing clear information about the origin and method of catch for their seafood.
- Offering variety: Including underutilised species to reduce pressure on popular stocks.
Through these practices, “Frozen Fish Direct” ensures that their offerings not only benefit consumers’ health but also contribute to the health of the planet.
Informed Seafood Selection for Expectant Mothers
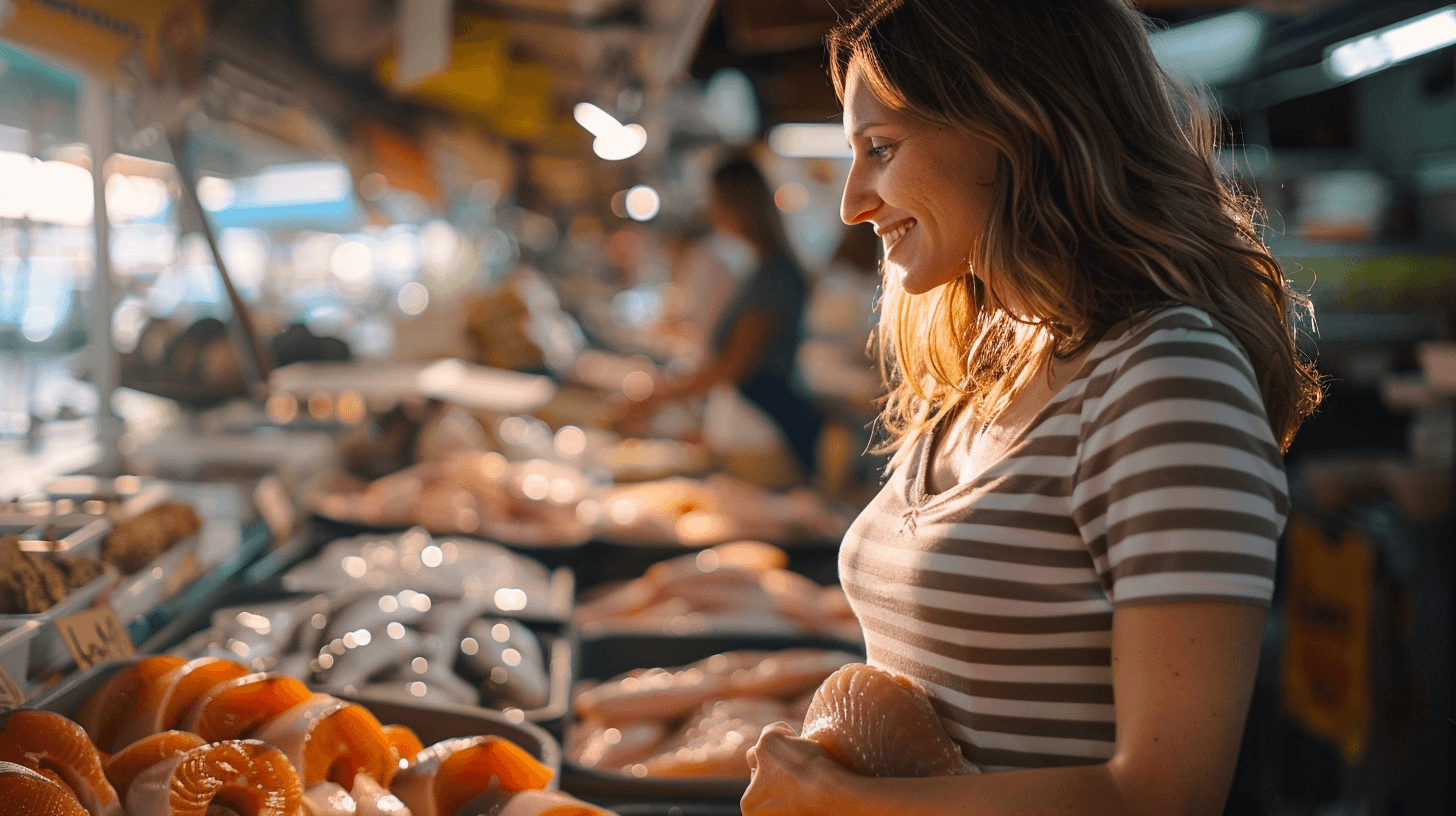

Expectant mothers can make informed decisions about seafood consumption by consulting the latest guidelines from trusted health organisations, such as the FDA and EPA, which recommend 8-12 ounces of low-mercury seafood per week. It’s essential to choose fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and tilapia, for their neurocognitive benefits to both mother and child.
Key Nutritional Takeaways for Prenatal Diets
Incorporating fish into a prenatal diet offers a multitude of benefits:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Critical for foetal brain and eye development.
- Protein: Supports overall growth and tissue repair.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Aid in the development of the baby and the well-being of the mother.
“Frozen Fish Direct” Support for Nutritional Choices
“Frozen Fish Direct” supports healthy choices for pregnant customers by:
- Providing a selection of low-mercury, high-nutrient seafood.
- Ensuring freshness and quality through rigorous sourcing standards.
- Offering detailed information on the nutritional content of their products.
Personalised Assistance and High-Quality Seafood Options
For personalised assistance and to explore high-quality seafood options, customers are encouraged to contact “Frozen Fish Direct.” Their team is equipped to provide guidance tailored to individual dietary needs, ensuring that you can confidently include the right seafood in your prenatal diet.









